Introduction
What is CubeFS ?
CubeFS is a next-generation cloud-native storage product that is currently an incubating open-source project hosted by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It is compatible with various data access protocols such as S3, POSIX, and HDFS, and supports two storage engines - multiple replicas and erasure coding. It provides users with multiple features such as multi-tenancy, multi-AZ deployment, and cross-regional replication, and is widely used in scenarios such as big data, AI, container platforms, databases, middleware storage and computing separation, data sharing and data protection.
Why CubeFS ?
Multi-protocol
Compatible with various access protocols such as S3, POSIX, and HDFS, and access between protocols is interoperable.
POSIX compatible: Compatible with the POSIX interface, making application development extremely simple for upper-layer applications, just as convenient as using a local file system. In addition, CubeFS relaxed the consistency requirements of POSIX semantics during implementation to balance the performance of file and metadata operations.
S3 compatible: Compatible with the AWS S3 object storage protocol, users can use the native Amazon S3 SDK to manage resources in CubeFS.
HDFS compatible: Compatible with the Hadoop FileSystem interface protocol, users can use CubeFS to replace the Hadoop file system (HDFS) without affecting upper-layer business.
Multi-engine
Supporting two engines: multi-replicas and erasure coding, users can flexibly choose according to their business scenarios.
- Multiple replicas storage engine: The data between copies is in a mirror relationship, and the consistency of data between copies is ensured through a strongly consistent replication protocol. Users can flexibly configure different numbers of copies according to their application scenarios.
- Erasure coding storage engine:Erasure coding engine has the characteristics of high reliability, high availability, low cost, and supports ultra-large scale (EB). According to different AZ models, erasure coding modes can be flexibly selected.
Multi-tenant
Supporting multi-tenant management and providing fine-grained tenant isolation policies.
Highly Scalable
It can easily build distributed storage services with PB or EB level scale, and each module can be horizontally scaled.
High-performance
CubeFS supports multi-level caching to optimize small file access and supports multiple high-performance replication protocols.
- Metadata management:The metadata cluster uses in-memory metadata storage and uses two B-Trees (inodeBTree and dentryBTree) to manage indexes to improve metadata access performance.
- Strong consistency replication protocol:CubeFS adopts different replication protocols according to the file write mode to ensure data consistency between replicas. If the file is written sequentially, the primary-backup replication protocol is used to optimize IO throughput. If the file is randomly written to overwrite existing file content, a replication protocol based on Multi-Raft is used to ensure strong consistency of data.
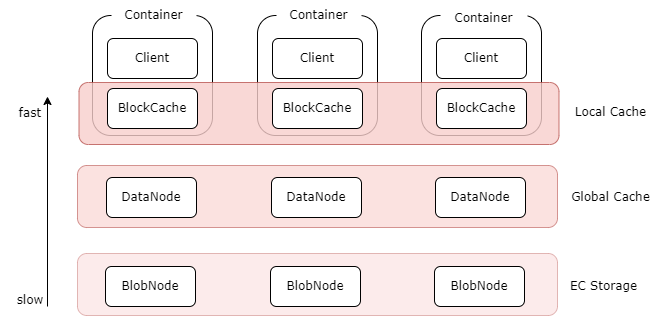
- Multi-level caching:The erasure coding volume supports multi-level caching acceleration capability to provide higher data access performance for hot data:
- Local cache: BlockCache component can be deployed on the client machine as a local cache using the local disk. It can directly read the local cache without going through the network, but the capacity is limited by the local disk.
- Global cache: A distributed global cache built using the replica component DataNode. For example, a DataNode with an SSD disk deployed in the same data center as the client can be used as a global cache. Compared with the local cache, it needs to go through the network, but it has a larger capacity and can be dynamically scaled, and the number of replicas can be adjusted.
cloud-native
Based on the CSI plugin, CubeFS can be quickly used on Kubernetes.
Application Scenarios
As a cloud-native distributed storage platform, CubeFS provides multiple access protocols, so it has a wide range of use cases. Below are some typical cases:
Big Data Analytics
Compatible with the HDFS protocol, CubeFS provides a unified storage foundation for the Hadoop ecosystem (such as Spark and Hive), providing unlimited storage space and high-bandwidth data storage capabilities for computing engines.
Deep Learning/Machine Learning
As a distributed parallel file system, CubeFS supports AI training, model storage and distribution, IO acceleration and other requirements.
Container Shared Storage
The container cluster can store the configuration files or initialization loading data of container images on CubeFS, and read them in real-time when batch loading containers. Multiple PODs can share persistent data through CubeFS, and quick fault switching can be performed in case of POD failure.
Database & Middleware
Provides high-concurrency, low-latency cloud disk services for database applications such as MySQL, ElasticSearch, and ClickHouse, achieving complete separation of storage and computing.
Online Services
Provides high-reliability, low-cost object storage services for online businesses (such as advertising, click-streams, and search) or end-users' graphics, text, audio, and video content.
Traditional NAS to Cloud
Replace traditional local storage and NAS offline and help IT business move to the cloud.