Architecture
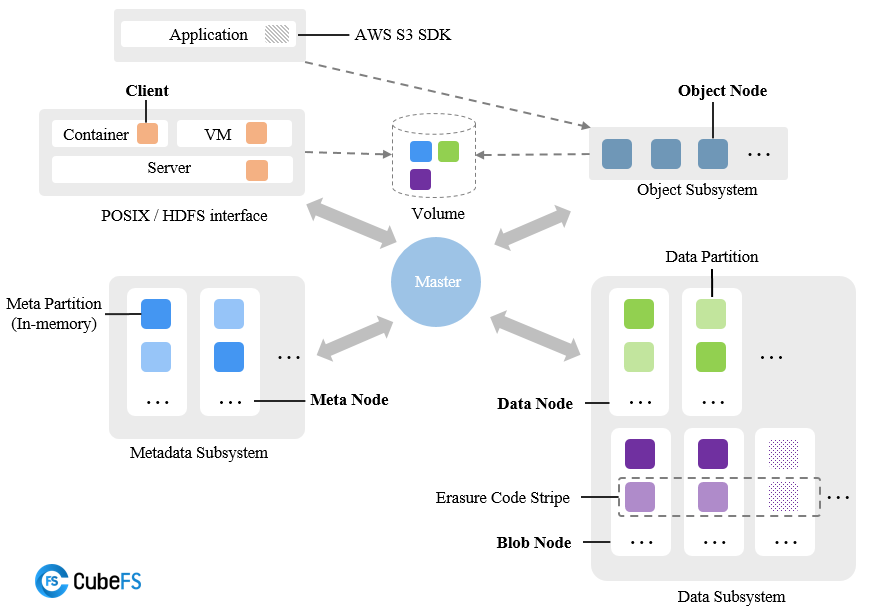
CubeFS consists of a metadata subsystem, a data subsystem, a resource management node (Master), and an object gateway (Object Subsystem), which can access stored data through the POSIX/HDFS/S3 interface.
- Resource Management Node: Composed of multiple Master nodes, it is responsible for asynchronously processing different types of tasks, such as managing data shards and metadata shards (including creation, deletion, updating, and consistency checks), checking the health status of data or metadata nodes, and maintaining volume information.
Note
There can be multiple Master nodes, and the consistency of metadata is ensured through the Raft algorithm and persisted to RocksDB.
- Metadata Subsystem: Composed of multiple Meta Node nodes, multiple metadata shards (Meta Partition), and Raft instances (based on the Multi-Raft replication protocol), each metadata shard represents an Inode range metadata, which contains two in-memory B-Tree structures: inode B-Tree and dentry B-Tree.
Note
At least 3 metadata instances are required, and horizontal scaling is supported.
- Data Subsystem: Divided into Replica Subsystem and Erasure Code Subsystem, both subsystems can coexist or exist independently:
- The Replica Subsystem consists of DataNodes, with each node managing a set of data shards. Multiple nodes' data shards form a replica group.
- The Erasure Code Subsystem (Blobstore) is mainly composed of BlobNode modules, with each node managing a set of data blocks. Multiple nodes' data blocks form an erasure-coded stripe.
Note
DataNode support horizontal scaling.
Object Subsystem: Composed of object nodes, it provides an access protocol compatible with standard S3 semantics and can be accessed through tools such as Amazon S3 SDK or s3cmd.
Volume: A logical concept composed of multiple metadata and data shards. From the client's perspective, a volume can be seen as a file system instance that can be accessed by containers. From the perspective of object storage, a volume corresponds to a bucket. A volume can be mounted in multiple containers, allowing files to be accessed by different clients simultaneously.