flash cluster
In the context of modern large AI model training, the scale of datasets and model parameters has increased dramatically. Local disk storage on a single GPU node is no longer capable of accommodating the TB- to PB-level data required for training. As a result, there is a growing need for a distributed caching strategy that offers greater capacity, higher throughput, and support for shared access across multiple GPU nodes, in order to enhance the efficiency of data retrieval during model training.
flash topology
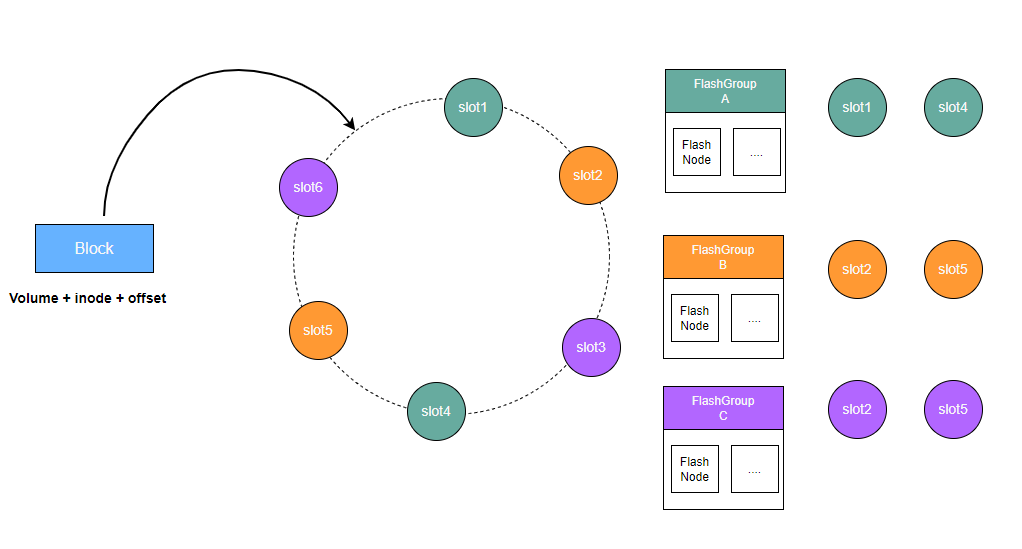
Data Access Flow
CubeFS's distributed cache is composed of multiple FlashGroups, each responsible for managing a set of slot values on the consistent hashing ring.
Clients calculate a unique value corresponding to the consistent hashing ring based on the volume ID, inode, and offset information of the data block to be cached. The distributed cache's routing algorithm then finds the first slot value on the ring that is greater than or equal to this calculated value. The FlashGroup owning that slot is responsible for persisting the data block and providing caching and read services for it.
A FlashGroup consists of cache nodes called FlashNodes, which can be deployed across different zones. When a client reads cached data, it performs latency analysis across the available FlashNodes and selects the one with the lowest access latency for the read operation.
FlashNode
The following shows an example of the configuration file used to launch the FlashNode process:
{
"role": "flashnode",
"listen": "18510",
"prof": "18511",
"logDir": "./logs",
"masterAddr": [
"xxx",
"xxx",
"xxx"
],
"memTotal": 0,
"cachePercent": 0.8,
"readRps": 100000,
"disableTmpfs": true,
"diskDataPath": [
"/path/data1:0",
"/path/data2:0"
],
"zoneName":"default"
}
Master
The Master manages the global topology of the distributed cache across the cluster, including persistent storage and centralized control. It monitors the status of each FlashNode by receiving registration and heartbeat messages. Furthermore, the Master supports slot assignment to FlashGroups via CLI commands. Clients retrieve the most up-to-date topology information from the Master to enable accurate routing of data read operations.
Client
In order to support file cache retrieval, the client evaluates both the per-volume cache configuration and the global caching state of the cluster before deciding to fetch data from the distributed cache.
Master
The Master is responsible for the persistent storage and unified management of the topology information of all distributed caches in the entire cluster. It receives registration information and heartbeat messages from FlashNodes to determine the survival status of each FlashNode. The Master accepts CLI commands for slot allocation of FlashGroups. When clients read data, they request the latest distributed cache topology from the Master to enable correct routing for data reading.
Client
To support file cache reading, the client determines whether to retrieve data from the distributed cache by combining the volume-level cache switch and the cluster cache function status.
flashGroupManager
Note
flashGroupManager is a new feature added in version 3.5.3.
The distributed cache management capabilities of the original Master are decoupled and separated into an independent component FlashGroupManager. This component provides upload/download services for object data blocks to the object storage engine; meanwhile, the Master reuses the capabilities of FlashGroupManager to implement unified orchestration and governance of CubeFS distributed cache resources.
FlashGroupManager: It is responsible for managing distributed cache resources, such as the registration of cache nodes (FlashNode), the creation of cache node replica groups (FlashGroup), and the configuration of distributed cache functions.
RemoteCacheClient: It provides data access services for the file storage and object storage engines in the form of an SDK.
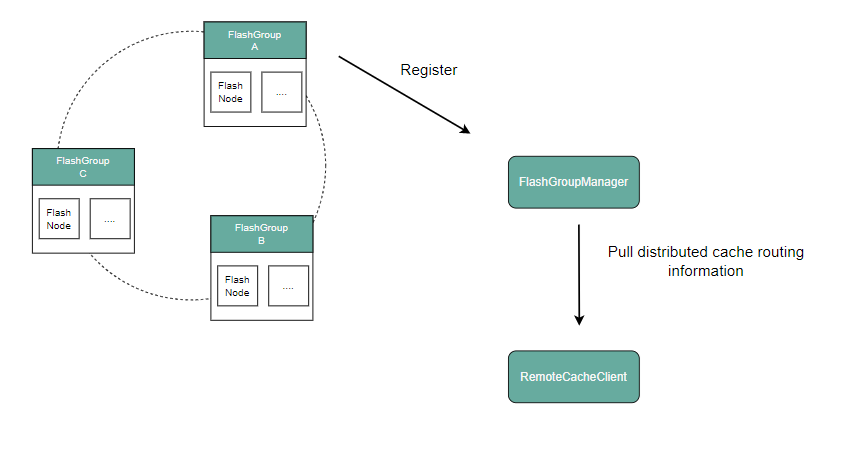
Upload and Download of Object Storage Data Blocks
You can refer to the code in tool/remotecache-benchmark of the code repository to implement the upload and download of object data blocks by initializing RemoteCacheClient and executing Put and Get operations.
Popularity Statistics
The Get method of RemoteCacheClient will inform the user whether it is necessary to upload data via Put based on the popularity statistics results of data blocks by FlashNode.
The Get method attempts to retrieve data: if the data is already cached, it returns the cached data; otherwise, it updates the popularity statistics.
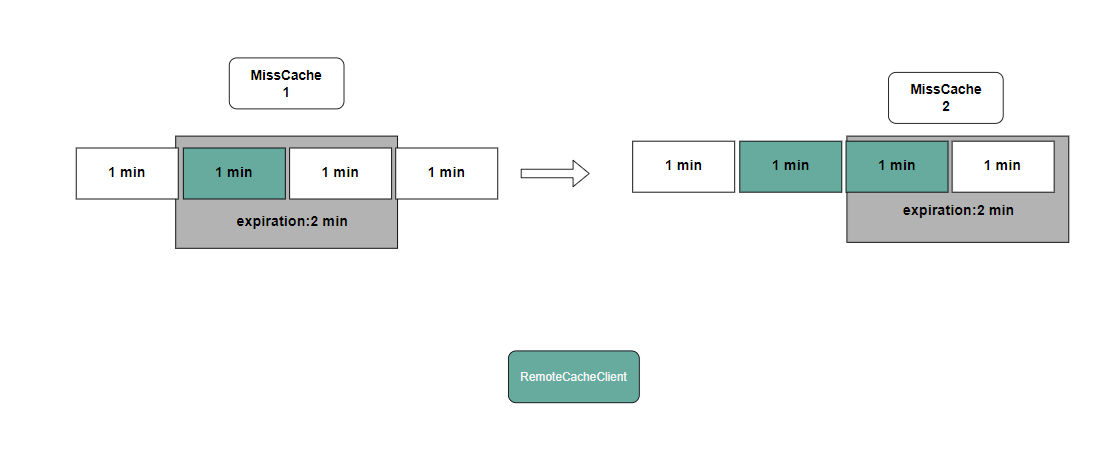
- If the popularity has not expired: increment the popularity count and refresh the expiration time to current time + 2 minutes.
- If the popularity has expired: reset the popularity count to 1 and set the expiration time to current time + 2 minutes.
- If no popularity information exists: create a new record with the popularity count set to 1 and the expiration time set to current time + 2 minutes.
If the popularity count reaches the configurable threshold within the rolling time window (2 minutes by default), the system will return ErrorNotExistShouldCache (data does not exist but should be cached). After receiving this error, the Put method can be called to upload the data block for subsequent access hits.